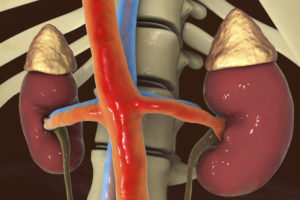
What is Adrenal Cancer?
Urologists diagnose and treat several forms of malignancies that can develop within the tubes and organs of the urinary system. Among these is adrenal cancer, a relatively rare form of cancer found in the adrenal glands. The adrenals are small, influential endocrine glands that are attached to the top of each kidney. These glands produce a host of hormones that help regulate metabolism, blood pressure, and sexual health, among other important functions.
Statistics from the American Cancer Society estimate that as little as 200 Americans are diagnosed with this cancer each year. Adrenal cancer affects men, women and children, with the average age of diagnosis being in the mid-40s.
Adrenal glands are made up of three parts: the outer fatty capsule, a lining beneath the capsule called the adrenal cortex, and the innermost section of the gland called the adrenal medulla. It is within the adrenal cortex where most tumors grow. These tumors are diagnosed as being either benign (Adenoma) or malignant (Carcinoma).
Diagnosis
There are several diagnostic tools that can be used to determine if a patient has adrenal cancer. When analyzing a patient, the provider will include a physical examination, a review of symptoms, medical history and laboratory testing of the blood and urine. In addition, imaging such as a CT scan, X-rays, Ultrasound, PET (Positron Emission Tomography) or MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) may be ordered. If the suspicious tumor is located on the outside of the adrenal gland, the provider may also perform a biopsy.
Because the adrenal glands produce hormones that affect several systems and functions of the human body, there is a diverse list of symptoms that could point to adrenal cancer. These symptoms may be related to hormonal changes, elevated blood pressure or sugar levels, weight changes, weakness, bruising, or unexplained pain.
Adrenal cancer treatment
There are several treatment options available for adrenal tumors. The most appropriate choice will be made depending on the size and location of the tumor, if the tumor is cancerous, and if it has moved outside the adrenal capsule into tissue, lymph nodes, bone, or to further locations. Treatment options include:
- Adrenalectomy – surgical removal of the adrenal gland (robotically or traditional laparoscopy)
- Radiation – as a secondary treatment following surgery, or to treat areas where adrenal cancer has spread (bone)
- Chemotherapy – for advanced stage adrenal cancer in conjunction with surgery, or as a first-line treatment when cancer was diagnosed after it had already metastasized to distant locations
If you are experiencing ongoing, unexplained changes in your urological health, contact Urology Austin to schedule a consultation with one of our providers.